It is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. The canal is approximately an inch in length. parts of the exterior ear.
Parts Of The Exterior Ear, Common characteristics of outer ear pain outer ear pain symptoms may present with: The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. The croswodsolver.com system found 25 answers for external part of the ear crossword clue.
 External Ear From fpnotebook.com
External Ear From fpnotebook.com
There are three different parts to the outer ear; This is the outside part of the ear. The outer ear is also composed of a canal that runs from the eardrum to the outside of the head.
The outer ear is made up of three parts, one of which is visible.
Tympanic cavity plays a significant role in an individual’s aptitude to hear. The purpose of the pinna is to catch sound waves, amplify them slightly, and funnel them down the ear canal to. This is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside. It is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. External, although it may seem devoid of many structures, also has a lot. The outer ear is the external part of the ear.
Another Article :

Auricle (cartilage covered by skin placed on opposite sides of the head) auditory canal (also called the ear canal) eardrum outer layer (also called the tympanic membrane) the outer part of the ear collects sound. Part of the skull in which the inner ear is located. The major landmarks of the external ear are depicted in figure 1. There are three different parts to the outer ear; Important parts of the outer ear are the pinna, the ear canal and the ear drum. Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology Ear anatomy.

Together with the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, the pinna serves to amplify sound. The purpose of the pinna is to catch sound waves, amplify them slightly, and funnel them down the ear canal to. The outer ear is also composed of a canal that runs from the eardrum to the outside of the head. Ear canal the ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The parts of the ear include: 25 Unique Ear Pinna.

The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. The canal is approximately an inch in length. The croswodsolver.com system found 25 answers for external part of the ear crossword clue. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna. The inferior portion is the lobule. Hearing and Vestibular Sensation OpenStax Biology 2e.

It is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. The outer ear consists of the visible portion on the side of the head, known as the pinna [1], and the external auditory canal (ear canal) [2]. The major landmarks of the external ear are depicted in figure 1. Includes the ossicles, three minuscule bones called the malleus, incus and stapes (the latter being the. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and to direct them into the ear. 5. External ear msn.
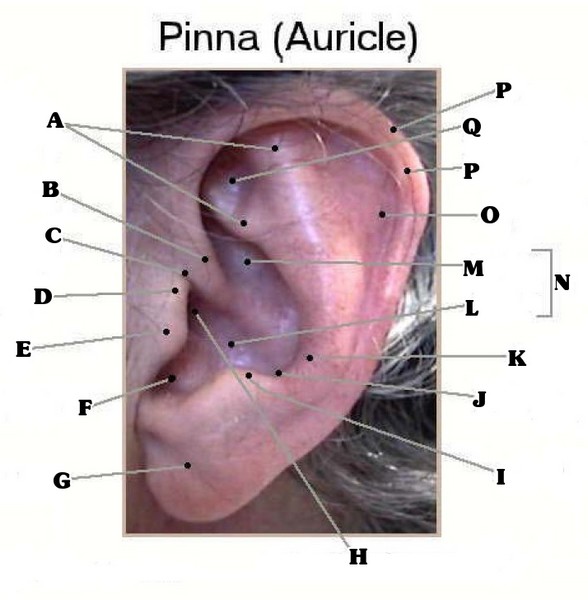
The canal is approximately an inch in length. If any portion of this system is harmed, it can be difficult to hear, or the patient can lose hearing in that ear all together. The rim of the auricle is the helix; The tragus, helix and the lobule. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna. Outer Ear Anatomy ProProfs Quiz.

The external ear can be divided functionally and structurally into two parts; It consists of the auricle and external acoustic meatus (or ear canal). The croswodsolver.com system found 25 answers for external part of the ear crossword clue. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and to direct them into the ear. There are three different parts to the outer ear; Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes.

The outer ear is the external part of the ear. The outer ear is also composed of a canal that runs from the eardrum to the outside of the head. The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. The outer ear is made up of three parts, one of which is visible. The anatomy of the external ear, also known as the auricle or pinna, is complex [hunter and yotsuyanagi, ] and remarkably inaccurately described by most authors. Middle Ear Anatomy and Physiology of Ear.

The pinna acts as a funnel to deliver sound to the external acoustic meatus, and the. Tympanic cavity plays a significant role in an individual’s aptitude to hear. The former projects from the side of the head and serves to collect the vibrations of the air by which sound is produced; Common characteristics of outer ear pain outer ear pain symptoms may present with: Parts of the ear external (outer) ear the external (outer) ear consists of the auricle, external auditory canal, and eardrum (figure 1 and 2). Anyone else notice physical appearance changes recently.
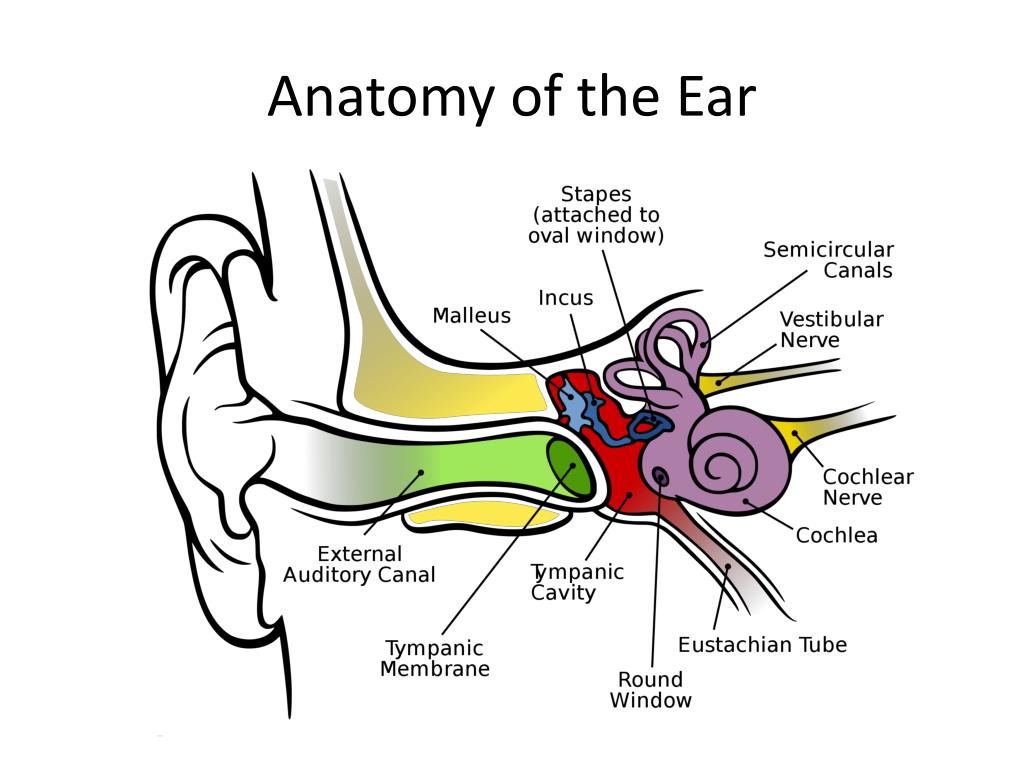
The pinna acts as a funnel to deliver sound to the external acoustic meatus, and the. The pinna is the part of the ear that sits on the outside of the head. At the bottom of the ear canal is the tympanic membrane which establishes the. The anatomy of the external ear, also known as the auricle or pinna, is complex [hunter and yotsuyanagi, ] and remarkably inaccurately described by most authors. Parts of the external ear study flashcards learn write spell test play match gravity created by annie_burtonplus terms in this set (12) auricle pinna auricle cartilagenous frame covered by. PPT The Ear PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID.

Eardrum is a biological membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear. The lobule consists of adipose and fibrous tissues supplied with blood capillaries. The croswodsolver.com system found 25 answers for external part of the ear crossword clue. External auditory canal or tube. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna. A Pediatrician’s Tips for Preventing Ear Infections This.

The parts of the ear include: Formed by the pinna and the external auditory canal, which receives sounds and transmits them to the middle ear via the eardrum.the eardrum is circular and flexible, and begins to vibrate as the incoming sound waves strike it. The former projects from the side of the head and serves to collect the vibrations of the air by which sound is produced; Noise or ringing in the ears. Ear canal the ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. External Ear.
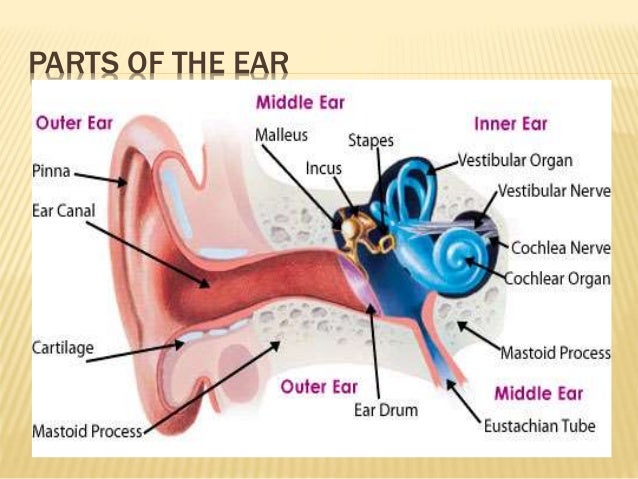
The external ear consists of skin (with adnexa), cartilage, and six intrinsic muscles. The outer ear is the external part of the ear. The former portion of the auditory system is the first point at. The external ear consists of skin (with adnexa), cartilage, and six intrinsic muscles. There is a cartilaginous portion, known as the pinna or auricle and a bony, tubular segment called the external acoustic meatus. The human ear.
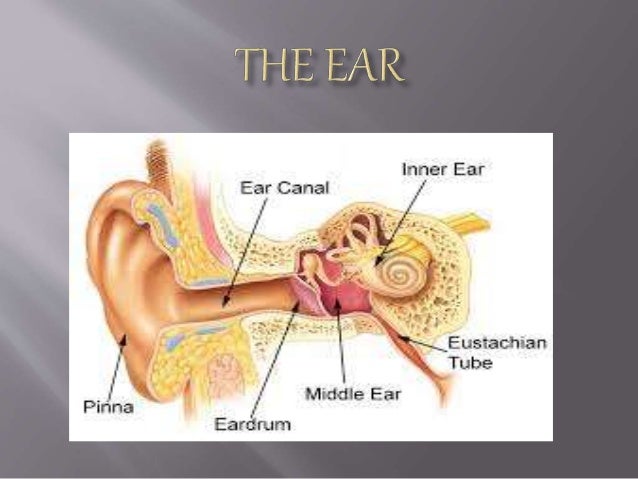
External auditory canal or tube. Together with the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, the pinna serves to amplify sound. The external ear is further divided into the following parts: The major landmarks of the external ear are depicted in figure 1. The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna. Science 3 parts of the ear.
Eardrum is composed of connective tissues covered with skin outside and with the mucous membrane inside. Noise or ringing in the ears. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. There are three different parts to the outer ear; The external ear comprises of two components. Labeled Diagram Of The Interior Of A Human Ear For.

Part of the skull in which the inner ear is located. The external ear is further divided into the following parts: If any portion of this system is harmed, it can be difficult to hear, or the patient can lose hearing in that ear all together. Eardrum is composed of connective tissues covered with skin outside and with the mucous membrane inside. The lobule consists of adipose and fibrous tissues supplied with blood capillaries. Hearing and Vestibular Sensation Biology II.










