Have the patient lie on the side of the head that is affected to promote drainage. The fibrocartilaginous auricle funnels sound waves from the environment into the auditory canal to the tympanic membrane. exterior ear anatomy.
Exterior Ear Anatomy, Supreet singh nayyar, afmc ms (ent) 2. External ear superficial landmarks, medially and laterally. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure.
 14.1 Sensory Perception Anatomy and Physiology From opentextbc.ca
14.1 Sensory Perception Anatomy and Physiology From opentextbc.ca
The external ear functions to collect and amplify sound, which then gets transmitted to the middle ear. Otoplasty | auricular deformities, specifically, prominent ears, are relatively frequent. Supreet singh nayyar, afmc ms (ent) 2.
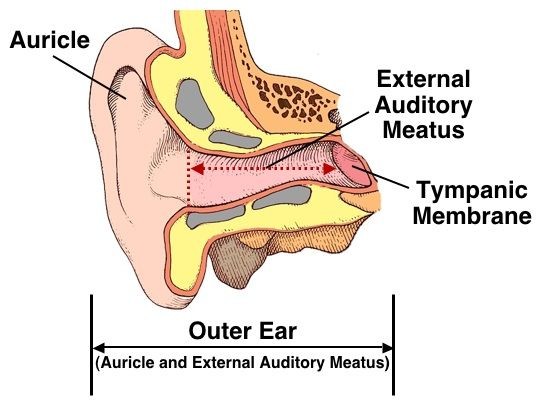
The external ear comprises the auricle and the auditory canal.
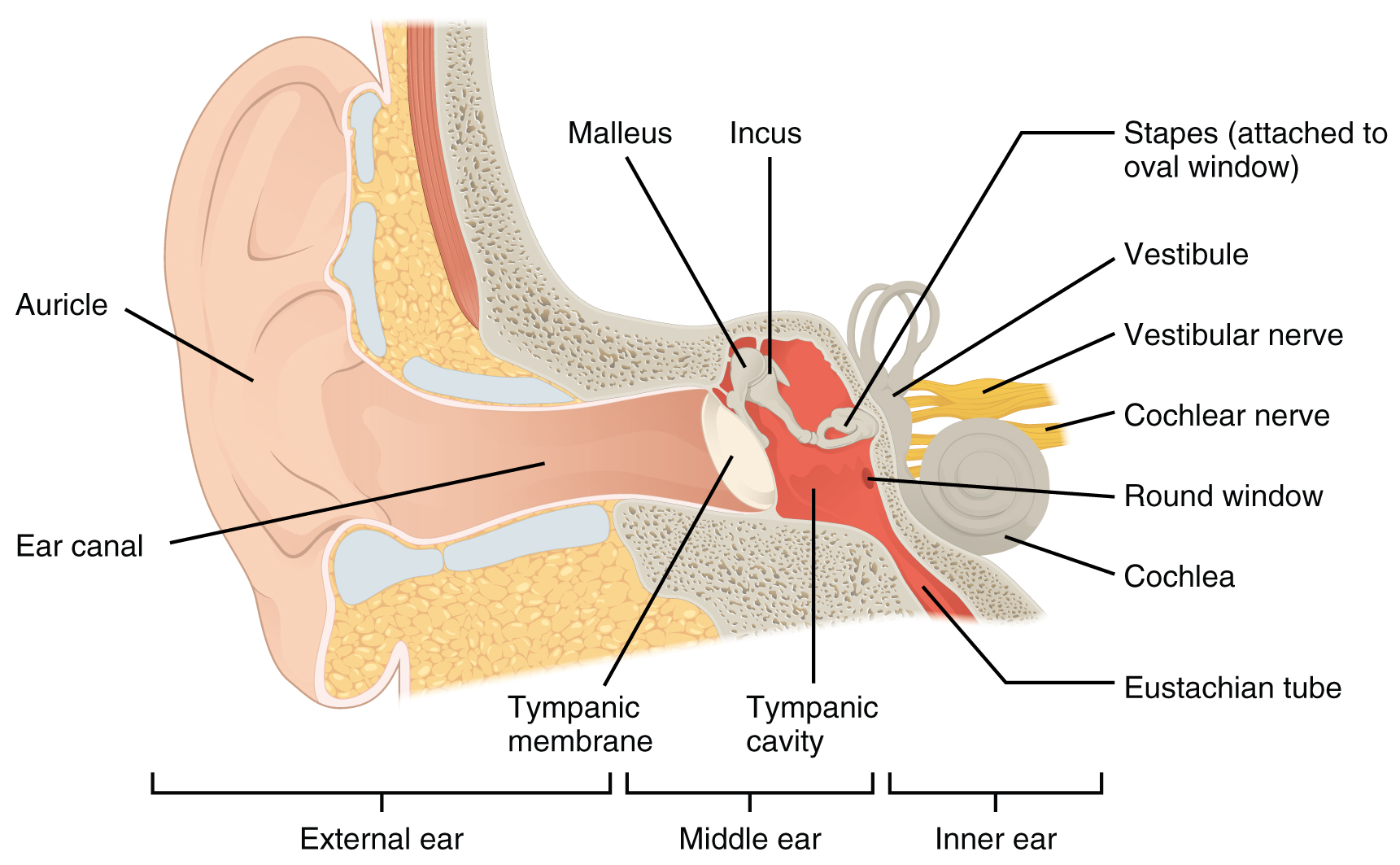
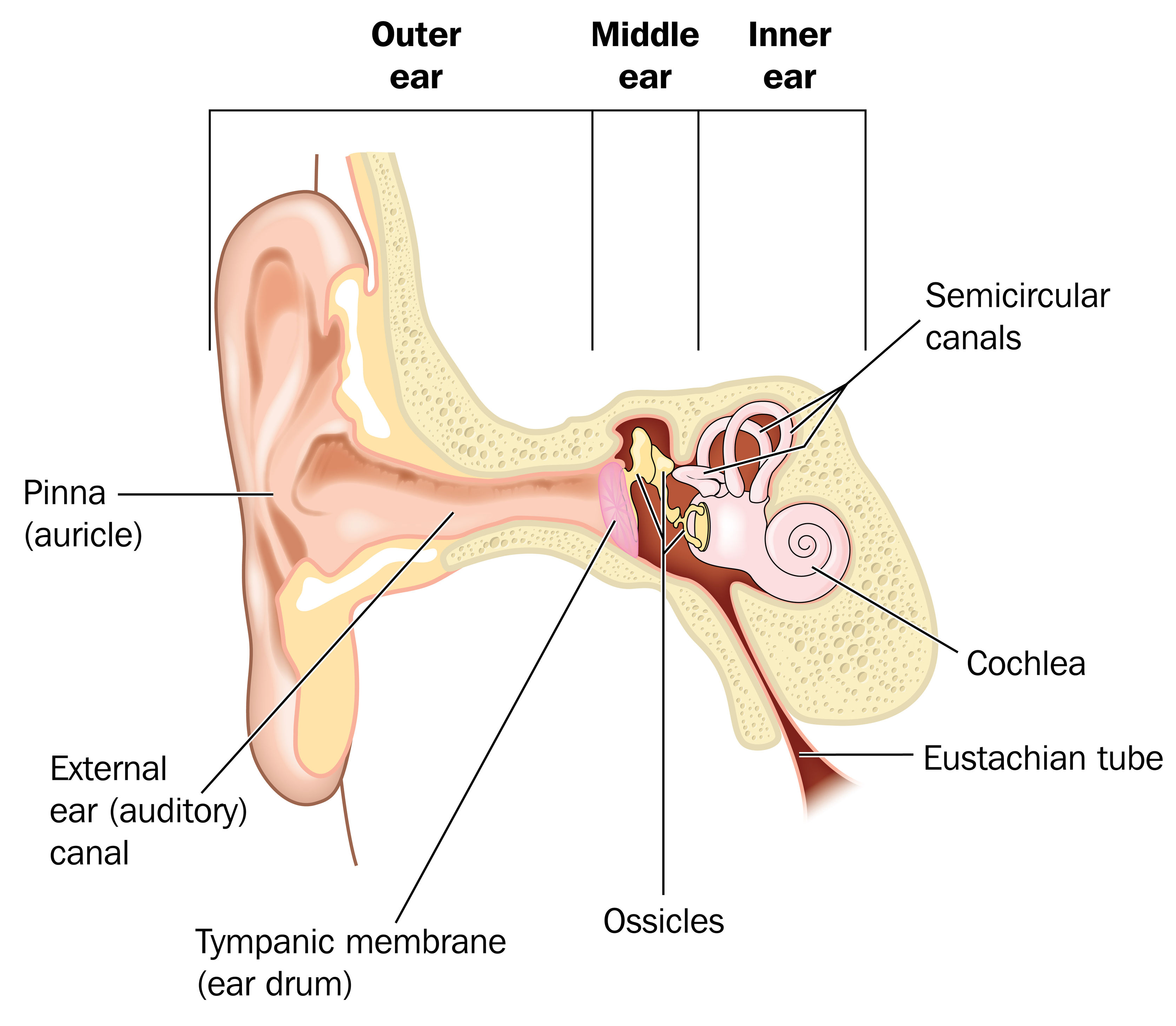
External ear it consists of auricle (pinna) and external acoustic meatus(eam). Parts of the ear by anatomy next. External ear superficial landmarks, medially and laterally. The major landmarks of the external ear are depicted in figure 1. The fibrocartilaginous auricle funnels sound waves from the environment into the auditory canal to the tympanic membrane. There are three different parts to the outer ear;
Another Article :

Do not allow the patient to thump his head to restore lost hearing. It is also sometimes referred to as the auricle or the pinna. Otoplasty | auricular deformities, specifically, prominent ears, are relatively frequent. Auris externa) is the outer part of each ear consisting of the auricle and external acoustic meatus. The external ear is the part of the ear we can see with the naked eye. Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes.
Deviations from the norm or aberrations in position, shape, size. The external ear consists of skin (with adnexa), cartilage, and six intrinsic muscles. The auricle concentrates and amplifies sound waves and funnels them through the outer acoustic pore into the external auditory meatus to the tympanic membrane. All three parts of the ear are important for detecting sound by working together to move sound from the outer part through the middle and into the inner part. The auricle and external acoustic meatus (or external auditory canal) compose the external ear. Anatomy of external ear.

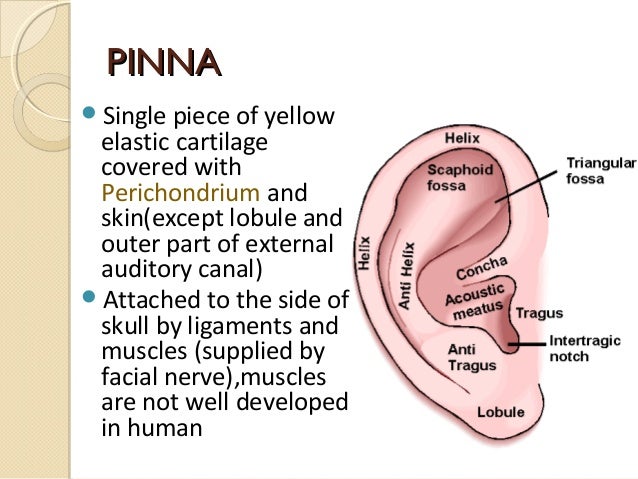
The external ear has a cartilaginous framework in all areas except the lobule. The outer curvature of the superior half of the auricle is the helix and is concave laterally. The antihelix is the next structure inward and is concave medially. The external ear (or outer ear) comprises the auricle (or pinna), the external auditory meatus, and the tympanic membrane (eardrum). Internal auditory canal and cerebellopontine angle; Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology Ear anatomy, Human.

External ear middle ear (cleft) inner ear. At the bottom of the ear canal is the tympanic membrane which establishes the border between the external and middle ear. Anatomy of the external ear. The external ear functions to collect and amplify sound, which then gets transmitted to the middle ear. The anatomy of the external ear, also known as the auricle or pinna, is complex [hunter and yotsuyanagi, ] and remarkably inaccurately described by most authors. Infant Ear Deformities and Malformations EarWell Centers.

The external ear has a cartilaginous framework in all areas except the lobule. The tragus, helix and the lobule. Anatomy ofanatomy of external earexternal ear 2. The major landmarks of the external ear are depicted in figure 1. Introduction hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor 3. CorePendium An Emergency Medicine Origin Story.
Hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor parts pinna external ear eac middle. The external ear includes the auricle and the eac. If bleeding is from the external ear, it may be controlled by direct pressure with a sterile or clean cloth. The external ear is the part of the ear we can see with the naked eye. The outer ear is made up of cartilage and skin. Ear infections explained Dr Mark McGrath.

Supreet singh nayyar, afmc ms (ent) 2. Introduction hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor 3. Surgical anatomy of the ear. Anatomy of the external ear. Supreet singh nayyar, afmc ms (ent) 2. Anyone else notice physical appearance changes recently.

Earear external ear middle ear inner ear 4. At the deep end of the external acoustic meatus, separating the external ear from the middle ear, lies the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The asymmetric shape of the external auricle introduces delays in the path of sound that assist in sound localization. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure. Anatomy of the external ear. 25 Unique Ear Pinna.

Deviations from the norm or aberrations in position, shape, size. The auricle and external acoustic meatus (or external auditory canal) compose the external ear. The ears are located on the lateral sides of the head. Introduction hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor 3. The auricle is mostly made up of cartilage that is covered with skin.there are two aspects of the. External Ear.

Auris externa) is the outer part of each ear consisting of the auricle and external acoustic meatus. The skin of the ear canal is very sensitive to pain and pressure. The external ear is the part of the ear we can see with the naked eye. Earear external ear middle ear inner ear 4. The auricle or pinna and the external acoustic meatus (more commonly referred to as the ear canal ). Ch 3 Vid 5 Anatomy of the ear YouTube.

The asymmetric shape of the external auricle introduces delays in the path of sound that assist in sound localization. The antihelix is the next structure inward and is concave medially. The auricle collects the sound waves and eam conducts them to the tympanic membrane. Anatomy ofanatomy of external earexternal ear 2. Deviations from the norm or aberrations in position, shape, size. 14.1 Sensory Perception Anatomy and Physiology.
Introduction hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor 3. Auris externa) is the outer part of each ear consisting of the auricle and external acoustic meatus. The external ear has a cartilaginous framework in all areas except the lobule. The outer, middle, and inner ear. The auricle or pinna and the external acoustic meatus (more commonly referred to as the ear canal ). Understanding Hearing Shamim Ebrahim Inc.

Earear external ear middle ear inner ear 4. External ear superficial landmarks, medially and laterally. The fibrocartilaginous auricle funnels sound waves from the environment into the auditory canal to the tympanic membrane. The external ear consists of the expanded portion named the auricula or pinna, and the external acoustic meatus. Anatomy of external ear 1. Pin by Windy Rothmund on Head & Neck Anatomy Auditory.

Introduction hearing is a primitive sense and is essential in all animals well developed and well protected it needs a sound source, conducting mechanism, end organ and a central processor 3. The helix, antihelix, superior and inferior crus, the tragus and antitragus, the concha, and the external acoustic meatus all work together to funnel and direct sound waves from the world around you to the inner parts of your ears. Supreet singh nayyar, afmc ms (ent) 2. All three parts of the ear are important for detecting sound by working together to move sound from the outer part through the middle and into the inner part. The external ear is the part of the ear we can see with the naked eye. Free Vector Anatomy of external ear.

The external ear (or outer ear) comprises the auricle (or pinna), the external auditory meatus, and the tympanic membrane (eardrum). Auricle the auricle, also known as pinna, is a wrinkly musculocutaneous tissue that is attached to the skull and it functions to capture sound. In most mammals, the external ear is represented by a flap of tissue also known as the pinna. Ear canal the ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. The outer ear consists of three parts. Ear Definition, Anatomy & Ear Infection.