Find the measure of the unknown numbered interior and exterior angles in the given triangle below. It explains how to use it in a two column proof situa. exterior angle inequality theorem example.
Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem Example, The measure of exterior angle = sum of two opposite interior angles’ measure what is the exterior angle inequality theorem? An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. A use the exterior angle inequality theorem to list all angles whose measures are less than m 14.
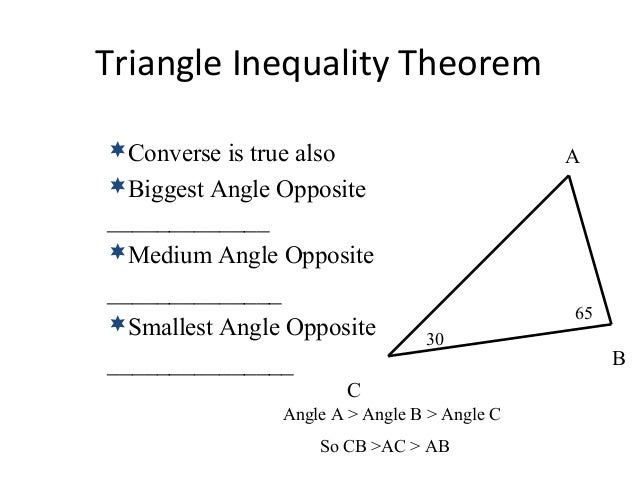
 Inequalities in One Triangle From geometrycoach.com
Inequalities in One Triangle From geometrycoach.com
In either case m∠1 6= m∠2 by the exterior angle inequality (theorem 1). ∠x is the exterior angle. Solve the inequality if ab + ac > bc example:
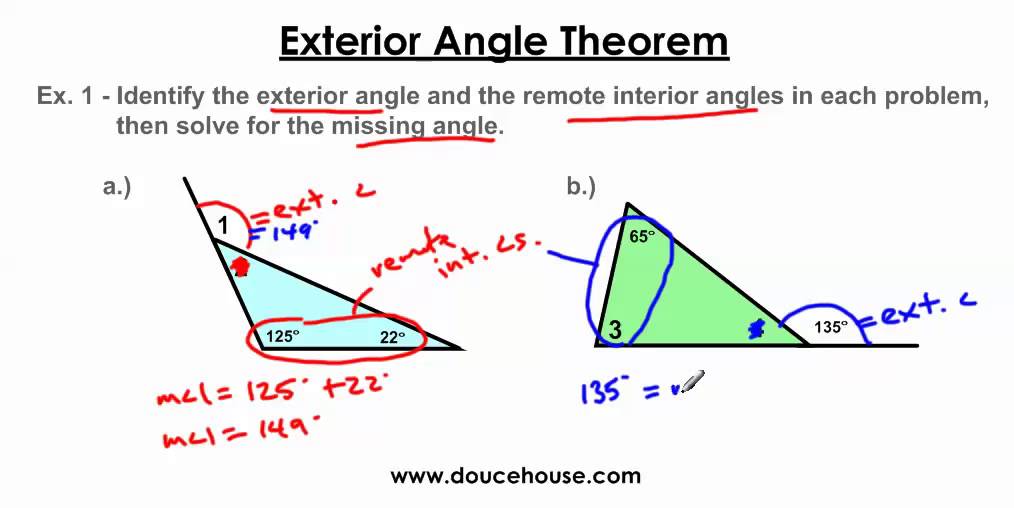
$16:(5 4 measures less than m 4 62/87,21 by the exterior angle inequality theorem, the exterior angle ( 4) is greater than either remote interior angle ( 1 and 2).therefore, m 1 < m 4 and m m 4.
Then either ∠1 is an exterior angle of 4abrand ∠2 is an interior angle opposite to it, or vise versa. Therefore, the values of x and y are 88º and 47º respectively. Since the angle across from segment is larger than the angle across from, is longer. Theorem 4.3 exterior angle theorem. Determine if the following lengths are legs of triangles 6 3 2 6 3 3 4 3 6 note that there is only one situation that you can have a triangle; 25*$1,=(,�($6 use the exterior angle inequality theorem to list all of the angles that satisfy the stated condition.
Another Article :

By the exterior angle inequality theorem, the exterior angle ( 5) is larger than either remote interior angle ( 7 and 8). Find the values of x and y in the following triangle. In this lesson, we will learn the triangle angle sum theorem the properties of an isosceles triangle the triangle inequality theorem the side inequalities and angle inequalities in a triangle exterior angles and remote interior angles of a triangle triangle angle sum the sum of the three angles in any triangle sum to 180 degrees. Theorem 4.4 properties of triangle congruence. ∆ inequalities date _____ per._____ 1.this is euclid’s proof that the exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either remote interior angle. Geometry Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem YouTube.

M∠1 + 92 ∘ = 180 ∘ through the linear pair postulate. Theorem 4.4 properties of triangle congruence. According to the external angle theorem, the measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two distant interior angles of a triangle. 6 example 1 use the outdoor angle inequality theorem 7 example 1 use the outer angle inequality theorem by the outer angle inequality theorem,. Exterior angle theorem worksheet pdf. PPT Chapter 5 Special Segments in Triangles PowerPoint.

An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. It explains how to use it in a two column proof situa. We know that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees. Take a look at the solved examples given below to understand the concept of the exterior angles and the exterior angle theorem. Inequality theorems of triangles the exterior angle inequality theorem states that an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of the remote interior angles. Exterior Angle Theorem and Triangle Inequality Theorem.

X e x e x e i i m x e m i x t e m i a 1 2 a t a t a t a t m x e i m a t let ∠ext be an extrior angle to ∆axe. Using the exterior angle theorem to solve problems. Remember the exterior angles theorem states that the exterior angle is congruent to the sum of the two non adjacent angles. ∆ inequalities date _____ per._____ 1.this is euclid’s proof that the exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either remote interior angle. $16:(5 4 measures less than m 4 62/87,21 by the exterior angle inequality theorem, the exterior angle ( 4) is greater than either remote interior angle ( 1 and 2).therefore, m 1 < m 4 and m m 4. EXAMPLE USING THE EXTERIOR ANGLE INEQUALITY THEOREM.

We know that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees. Take a look at the solved examples given below to understand the concept of the exterior angles and the exterior angle theorem. In the picture above, the gray region represents the interior of the triangle, and the. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. Find the values of x and y by using the exterior angle theorem of a triangle. Pin on exterior angle theorem calculator.

I hope it will help. Theorem 4.2 third angle theorem. A use the exterior angle inequality theorem to list all angles whose measures are less than m 14. Exterior angle theorem exterior angles of a triangle the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. The other arc, consisting of points exterior to angle poq, is called the major arc pq. Exterior Angle Inequality Theorem slidesharetrick.

According to the external angle theorem, the measure of an exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two distant interior angles of a triangle. M∠1 + 92 ∘ = 180 ∘ through the linear pair postulate. Taking our above example, (\angle {\text{acd}}) would equal whatever (\angle {\text{a}}) + (\angle {\text{b}}) equaled because those are the two angles not connected to the exterior angle. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. A use the exterior angle inequality theorem to list all angles whose measures are less than m 14. Inequalities in One Triangle.

We know that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees. L m t 1 2 r a b figure 2. M 2 and m 14 > This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the exterior angle inequality theorem. By the exterior angle inequality theorem, the exterior angle ( 5) is larger than either remote interior angle ( 7 and 8). Pin on exterior angle theorem hexagon.

This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the exterior angle inequality theorem. ∠x is the exterior angle. M 2 and m 14 > Therefore, m 7 < m 5 and m 8 < m $16:(5 7, 8 measures less than m 9 62/87,21 by the exterior angle inequality theorem, the exterior angle ( 9) is larger than either remote interior angle from two different triangles ( 6 and 7 from one triangle and and from. Then either ∠1 is an exterior angle of 4abrand ∠2 is an interior angle opposite to it, or vise versa. Pin on homedecor.

⇒ c + d = 180° ⇒ a + f = 180° ⇒ b + e = 180° all exterior angles of a triangle add up to 360°. Using the exterior angle theorem, find the value of x from the following figure. The sum of exterior angle and interior angle is equal to 180 degrees. According to the exterior angle inequality theorem, the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is greater than either of its interior opposite angles. This geometry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into the exterior angle inequality theorem. Inequalities in One Triangle.
⇒ d + e + f = b + a + a + c + b + c ⇒ d +e + f = 2a + 2b + 2c = 2(a + b + c) Find the values of x and y by using the exterior angle theorem of a triangle. X e x e x e i i m x e m i x t e m i a 1 2 a t a t a t a t m x e i m a t let ∠ext be an extrior angle to ∆axe. Hence, m∠1 = 88 ∘ Remember the exterior angles theorem states that the exterior angle is congruent to the sum of the two non adjacent. 5 2 triangle inequality theorem.
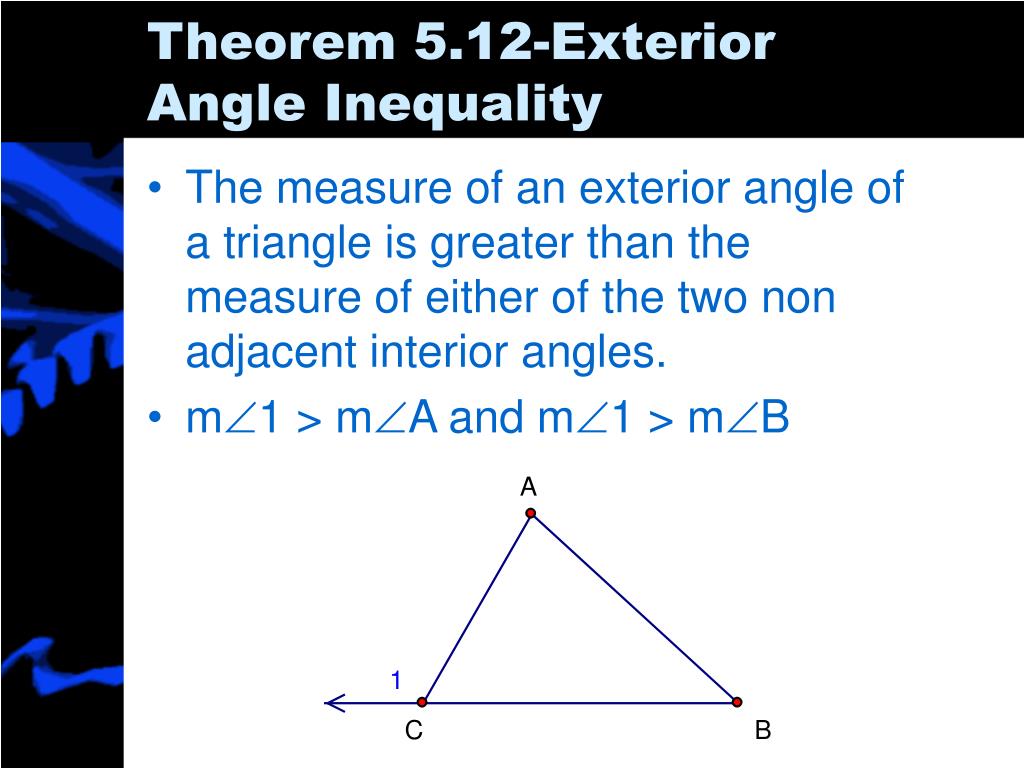
Using the exterior angle inequality theorem, what two things can be concluded with the following picture? M∠1 + 92 ∘ = 180 ∘ through the linear pair postulate. Using the exterior angle theorem, find the value of x from the following figure. 6 example 1 use the outdoor angle inequality theorem 7 example 1 use the outer angle inequality theorem by the outer angle inequality theorem,. M 4 and m 14 > PPT 5.5 Inequalities in One Triangle PowerPoint.

Hence, m∠1 = 88 ∘ The measure of a semicircle is =180 degrees. X x x 57 43 50 x 53 62 80 65 x 80 50 44 x title. Exterior angle theorem exterior angles of a triangle the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. Then either ∠1 is an exterior angle of 4abrand ∠2 is an interior angle opposite to it, or vise versa. D5 Triangle Inequality and Exterior Angle Theorem YouTube.
We know that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees. Determine if the following lengths are legs of triangles 6 3 2 6 3 3 4 3 6 note that there is only one situation that you can have a triangle; Solve the inequality if ab + ac > bc example: Taking our above example, (\angle {\text{acd}}) would equal whatever (\angle {\text{a}}) + (\angle {\text{b}}) equaled because those are the two angles not connected to the exterior angle. Geometry is a bit like a magician�s trick. Chapter 5 Review Perpendicular Bisector, Angle Bisector.
⇒ c + d = 180° ⇒ a + f = 180° ⇒ b + e = 180° all exterior angles of a triangle add up to 360°. M 4 + m 3, so m 14 > Acobdarfq and 212 more users found this answer helpful. Using the exterior angle inequality theorem, what two things can be concluded with the following picture? 25*$1,=(,�($6 use the exterior angle inequality theorem to list all of the angles that satisfy the stated condition. Exterior Angle Theorem YouTube.










