Interior angles on the same side of the transversal: Try this drag an orange dot at a or b. adjacent exterior angles.
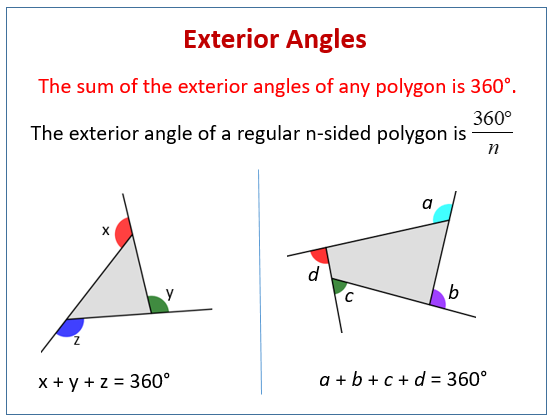
Adjacent Exterior Angles, The angles created between the side of the polygon and the extended adjacent side of the polygon are known as exterior angles.according to the external angle theorem, when a triangle’s side is stretched, the resulting exterior angle is equal to the sum of the measurements of the triangle’s two opposed internal. Try this drag an orange dot at a or b. Exterior angles are created where a transversal crosses two (usually parallel) lines.
 Corresponding, Alternate and CoInterior Angles (7 From alamandamaths.com
Corresponding, Alternate and CoInterior Angles (7 From alamandamaths.com
What is the measure of an exterior angle at the sixth vertex? Angle abc is adjacent to angle cbd because: Consecutive exterior angles these consecutive angles lie on the outside or exterior region of the two parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal.
How do we find the value of exterior angles?
Consecutive exterior angles these consecutive angles lie on the outside or exterior region of the two parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal. A diagonal line extends from angle 8 to form angle 2. (d and c, c and a, d and b, f and e, e and g, h and g,. Exterior angles of a polygon an exterior angle is formed by one of the sides of a polygon and the extension of the adjacent side. Alternate exterior angles are a pair of angles formed on the outside of two lines that are crossed by a third line. An exterior angle of the triangle is the angle between one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side.
Another Article :

⇒ (2x + 10) ° = 50° (x + 5) = 25° hence, (3x + 10) ° ≠ (x + 50) ° the two angles are not congruent. X = 20 now substitute x in each expression. The angles that are formed between one side of a quadrilateral and another line extended from an adjacent side are called its exterior angles. How can you use this fact as another method to fi nd the measure of each exterior angle in example 6? The name is a description of the location of the these angles. Interior Angles Solved Examples Geometry Cuemath.
(ii) exterior angles are the angles formed outside of a polygon when one of its sides is extended. The name is a description of the location of the these angles. The exterior angles of this pentagon are formed by extending its adjacent sides. It is adjacent to (beside) the interior angle. Consecutive exterior angles theorem : Angles Types Acute Angle Complementary Obtuse Cuemath.

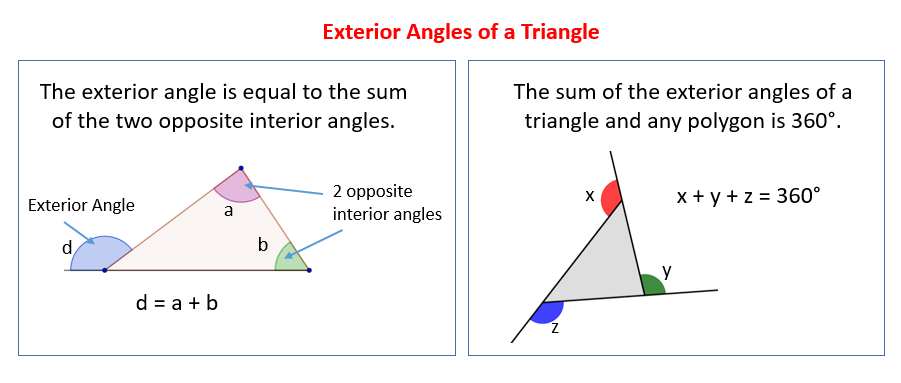
The theorem above states that if ∠4 is an exterior angle, its measure is equal to the sum of the measures of the 2 interior angles to which it is not adjacent, namely, ∠2 and ∠3. Together, the adjacent interior and exterior angles will add to 180° 180 °. The alternate angles are located on opposite sides of the transverse line. A convex hexagon has exterior angles with measures 34°, 49°, 58°, 67°, and 75°. Adjacent interior and exterior angles are supplementary angles. mrwadeturner / Sofia Pivaral journal 5.

In the above triangle, ∠ a ∠b ∠c are interior angles while ∠ d is an exterior angle. Similarly, since the angle measuring 60° adjacent to ∠4 form a straight angle, ∠4=120°. An exterior angle of a polygon is an angle at a vertex of the polygon, outside the polygon, formed by one side and the extension of an adjacent side. In other words, the sum of each interior angle and its adjacent exterior angle is equal to 180 degrees (straight line). The angles that are formed between one side of a quadrilateral and another line extended from an adjacent side are called its exterior angles. Interior adjacent angles YouTube.
Therefore, equate the two angles. What is the exterior angle theorem formula? Click to see full answer. Depending on the nature of the lines, the angles will have some characteristics. In the figure above, ∠1 and ∠8 are consecutive exterior angles, and also ∠2 and ∠7 are consecutive angles. Same Side Interior Angles Examples A polygon is a closed.

⇒ (3x + 10) ° = (x + 50) ° ⇒2 x = 40 divide both sides by 2. X = 20 now substitute x in each expression. What is the sum of the exterior angles of a triangle? Notice that the two exterior angles shown are supplementary (add to 180°) if the lines pq and rs are parallel. What is the measure of an exterior angle at the sixth vertex? Alternate exterior anglesDefinition & Examples Cuemath.
If we observe the figure given above, we can see that the exterior angle and interior angle form a straight line, and hence, they make a linear pair. An exterior angle is formed by one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side of the triangle. Adjacent interior and exterior angles are supplementary angles. Notice that the two exterior angles shown are supplementary (add to 180°) if the lines pq and rs are parallel. Each pair of these angles are outside the parallel lines, and on the same side of the transversal. Exterior Angles of Polygons (examples, solutions, videos.

For our equilateral triangle, the exterior angle of any vertex is 120° 120 °. Adjacent angles need one side in common so, ∠cbx and ∠fbc (or, to see it more easily,. The corresponding exterior angle is formed by one of these sides and continuation of another (see the drawing.) that makes these two angles adjacent to each other and together forming a straight angle of 180o degree. Supplementary means that the two angles add up to 180 degrees. Since you are extending a side of the polygon, that exterior angle must necessarily be supplementary to the polygon�s interior angle. 📈Which angles are adjacent angles to 3? Select all that.

Angle 6 has exterior angle. Adjacent interior and exterior angles are supplementary angles. Alternate exterior angles are a pair of angles formed on the outside of two lines that are crossed by a third line. Angle 7 has an exterior angle of 1. In the figure above, ∠1 and ∠8 are consecutive exterior angles, and also ∠2 and ∠7 are consecutive angles. Angles, areas and diagonals of regular polygons.
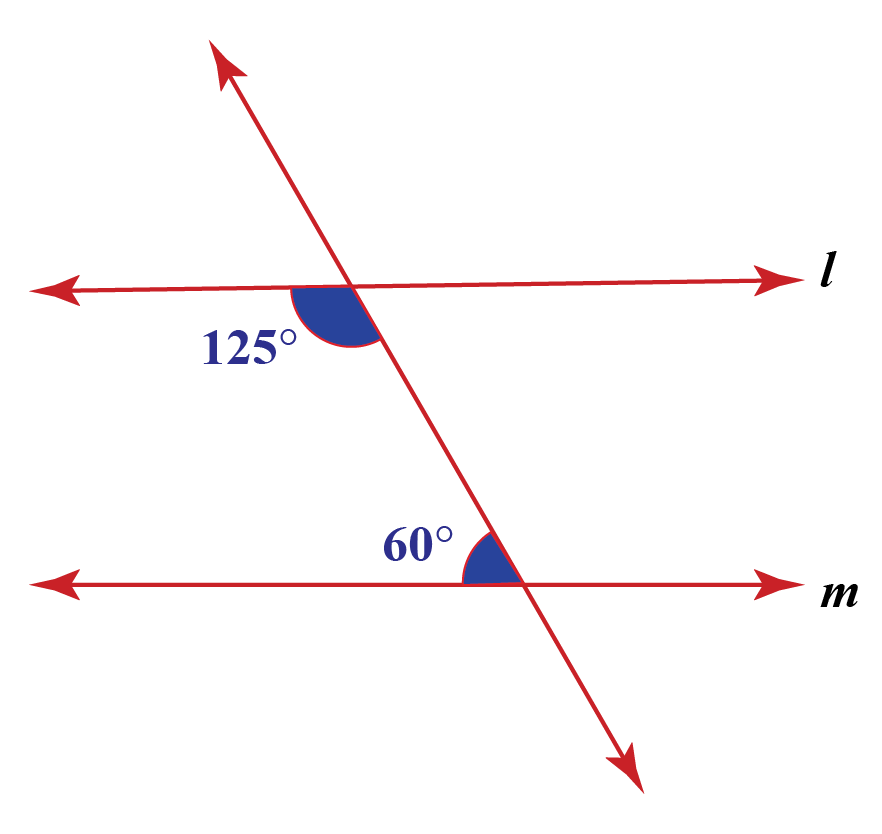
Exterior angles of a regular polygon are equal in measure. A diagonal line extends from angle 8 to form angle 2. Adjacent angles need one side in common so, ∠cbx and ∠fbc (or, to see it more easily,. For a square, the exterior angle is 90° 90 °. Notice that corresponding interior and exterior angles are supplementary (add to 180°). Transversal.

Exterior angles are created where a transversal crosses two (usually parallel) lines. Consecutive exterior angles these consecutive angles lie on the outside or exterior region of the two parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal. 147 views answer requested by azeezat adebayo allen ries , b.ed. A diagonal line extends from angle 8 to form angle 2. What is the measure of an exterior angle at the sixth vertex? Parallel Line Theorems GeoGebra.
The corresponding exterior angle is formed by one of these sides and continuation of another (see the drawing.) that makes these two angles adjacent to each other and together forming a straight angle of 180o degree. The theorem above states that if ∠4 is an exterior angle, its measure is equal to the sum of the measures of the 2 interior angles to which it is not adjacent, namely, ∠2 and ∠3. The angles that are formed between one side of a quadrilateral and another line extended from an adjacent side are called its exterior angles. How can you use this fact as another method to fi nd the measure of each exterior angle in example 6? As seen from the above picture, the two consecutive exterior angles are supplementary because the transversal line cuts the parallel lines. Exterior Angles of a Triangle (solutions, examples, videos).
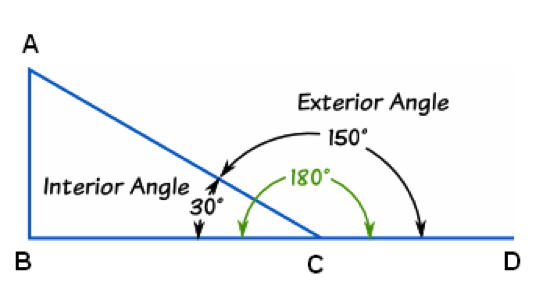
Try this drag an orange dot at a or b. Adjacent interior and exterior angles are supplementary angles. A diagonal line extends from angle 8 to form angle 2. Given below is the proof of the exterior angle theorem. The angles that are formed between one side of a quadrilateral and another line extended from an adjacent side are called its exterior angles. Understanding Angles and its Types.

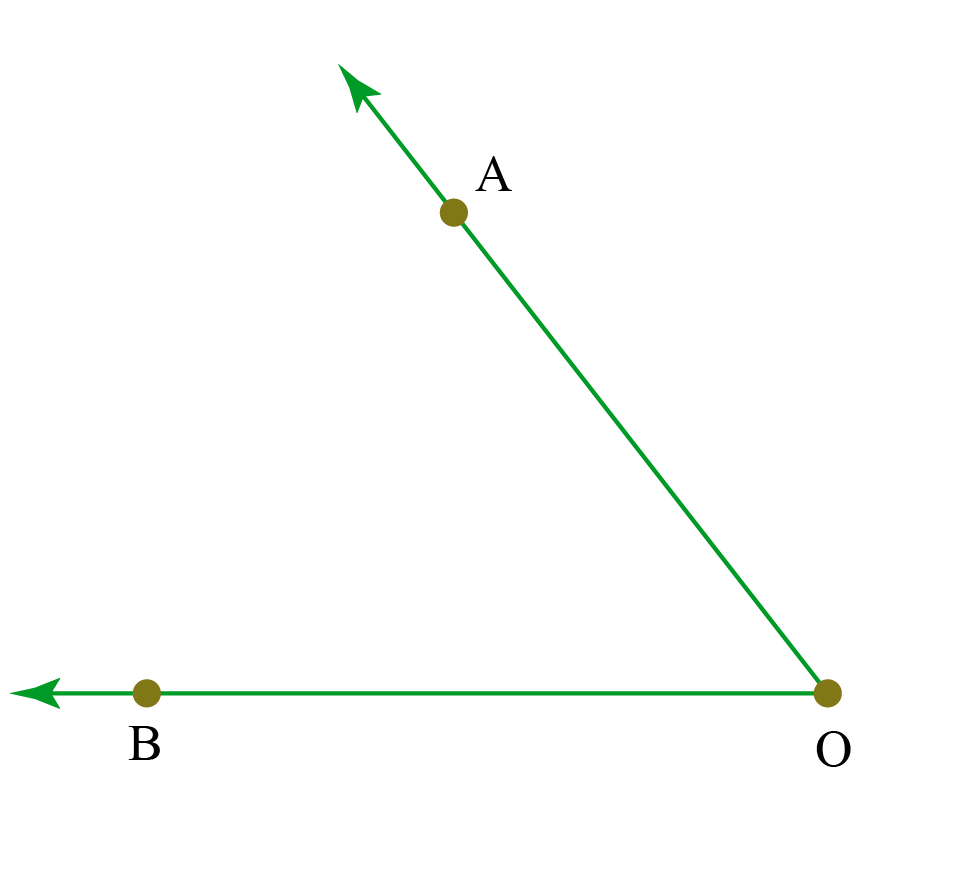
Together, the adjacent interior and exterior angles will add to 180° 180 °. Angle abc is adjacent to angle cbd because: An exterior angle of the triangle is the angle between one side of a triangle and the extension of an adjacent side. Try this drag an orange dot at a or b. Depending on the nature of the lines, the angles will have some characteristics. Q3 The given diagram shows two adjacent angles AOB and AOC.

In the above triangle, ∠ a ∠b ∠c are interior angles while ∠ d is an exterior angle. ⇒ (3x + 10) ° = (x + 50) ° ⇒2 x = 40 divide both sides by 2. Consecutive exterior angles theorem : From university of alberta (1974) ⇒ (2x + 10) ° = 50° (x + 5) = 25° hence, (3x + 10) ° ≠ (x + 50) ° the two angles are not congruent. Corresponding, Alternate and CoInterior Angles (7.










